Craft Stations
Craft Stations are nodes that manage the crafting process in your inventory system. They connect input inventories containing ingredients to output inventories where crafted products are placed, and they process Recipe resources to transform items over time.
Overview
A CraftStation node provides a complete crafting system that:
Filters available recipes based on station type
Validates ingredient availability before starting crafts
Manages multiple concurrent crafting processes
Handles timing and progression of crafts
Automatically moves ingredients and products between inventories
Provides signals for UI and game logic integration
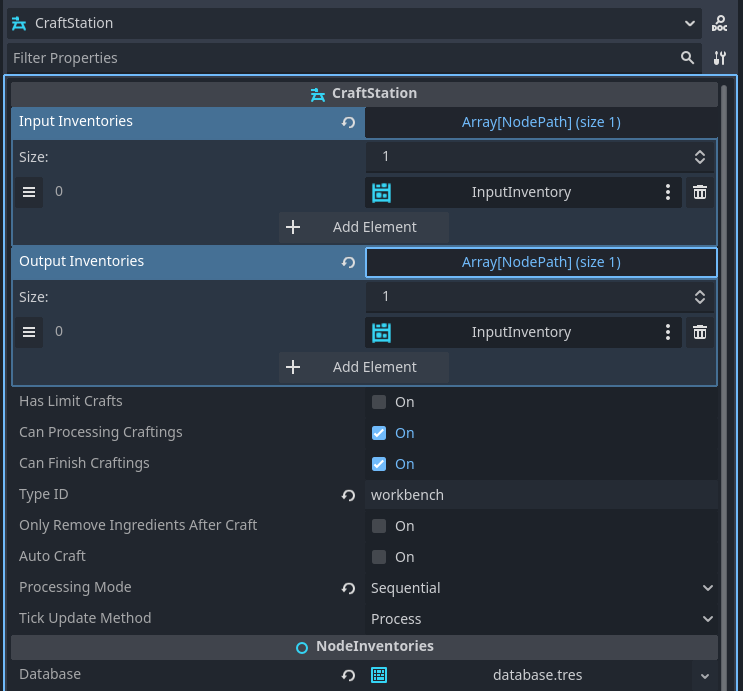
Key Components
Station Type
Each craft station can have a CraftStationType that determines which recipes it can process. This allows you to create specialized crafting stations like furnaces, workbenches, or alchemy tables.
Input Inventories
Input inventories provide the ingredients and required items for crafting. These are Inventory nodes that the craft station monitors for available materials.
Output Inventories
Output inventories receive the products when crafting completes. Products are automatically added to these inventories when a craft finishes successfully.
Note
Output inventories and Input inventories can be the same inventory.
Valid Recipes
The station automatically builds a list of recipes it can process based on:
Recipes in the connected InventoryDatabase
Station type compatibility
Current ingredient availability
Setting Up a Craft Station
Basic Setup
Add CraftStation Node
Add a CraftStation node to your scene.
Connect Database
Set the database property to your InventoryDatabase resource.
Add Inventories
Create Inventory nodes for inputs and outputs, then connect them to the craft station.
Configure Station Type (Optional)
Set the type property to a specific CraftStationType if you want to limit which recipes this station can process.
# Example: Basic craft station setup in code
@onready var craft_station = $CraftStation
@onready var input_inventory = $InputInventory
@onready var output_inventory = $OutputInventory
func _ready():
# Connect inventories
craft_station.add_input_inventory(input_inventory)
craft_station.output_inventories = [output_inventory.get_path()]
# Set station type (optional)
craft_station.type = "furnace"
Advanced Configuration
Processing Mode
Configure how multiple crafts are handled:
Sequential: Crafts process one at a time
Parallel: Multiple crafts process simultaneously
# Set processing mode
craft_station.processing_mode = CraftStation.ProcessingMode.PARALLEL
Craft Limits
Limit the number of concurrent crafts:
# Enable craft limits
craft_station.has_limit_crafts = true
craft_station.limit_number_crafts = 3
Auto Crafting
Enable automatic crafting when ingredients are available:
# Enable auto-crafting
craft_station.auto_craft = true
Note
This is used on campfire in fps demo.
Crafting Process
Starting a Craft
Crafting is initiated by calling the craft() method with a recipe index:
# Start crafting the first available recipe
if craft_station.valid_recipes.size() > 0:
craft_station.craft(0)
The system will:
Validate the recipe is available and ingredients are present
Remove ingredients from input inventories (unless only_remove_ingredients_after_craft is enabled)
Add a new Crafting process to the station’s list
Begin timing the craft duration
Craft Processing
Active crafts are processed based on the tick_update_method:
Process: Uses Godot’s
_process()callbackPhysics Process: Uses Godot’s
_physics_process()callbackCustom: Manual timing via code
# Example: Custom timing
craft_station.tick_update_method = CraftStation.TickUpdateMethod.CUSTOM
func _process(delta):
craft_station.tick(delta)
Note
Custom timing is important for multiplayer server games with ticks.
Finishing Crafts
When a craft completes:
Products are added to output inventories
Ingredients are removed (if only_remove_ingredients_after_craft is enabled)
The on_crafted signal is emitted
The craft is removed from the active list
Monitoring Crafting
Signals
CraftStation provides several signals for monitoring the crafting process:
func _ready():
# Connect to crafting signals
craft_station.on_request_craft.connect(_on_craft_requested)
craft_station.crafting_added.connect(_on_crafting_added)
craft_station.on_crafted.connect(_on_craft_completed)
craft_station.crafting_removed.connect(_on_crafting_removed)
func _on_craft_requested(recipe_index: int):
print("Craft requested for recipe: ", recipe_index)
func _on_crafting_added(crafting_index: int):
print("Crafting started: ", crafting_index)
func _on_craft_completed(recipe_index: int):
print("Craft completed for recipe: ", recipe_index)
func _on_crafting_removed(crafting_index: int):
print("Crafting removed: ", crafting_index)
Current Crafts
Monitor active crafting processes:
# Check if station is crafting
if craft_station.is_crafting():
print("Station is currently crafting")
# Get current crafting processes
for i in craft_station.craftings.size():
var crafting = craft_station.craftings[i]
var progress = crafting.get_time() / recipe.time_to_craft
print("Craft ", i, " progress: ", progress * 100, "%")
Recipe Availability
Check which recipes are available:
# Get available recipes
for recipe_index in craft_station.valid_recipes:
var recipe = database.recipes[recipe_index]
var can_craft = craft_station.can_craft(recipe)
print("Recipe: ", recipe.name, " - Can craft: ", can_craft)
Best Practices
Performance
Use appropriate tick_update_method for your needs
Limit concurrent crafts for complex recipes
Consider using Custom tick method for precise timing control
User Experience
Provide clear visual feedback for crafting progress
Use signals to update UI elements
Consider auto-crafting for convenience features
Game Balance
Set appropriate craft times for pacing
Balance ingredient requirements with output value
Use station types to create progression systems
See also
Recipes - Learn about creating recipes
CraftStationType - Learn about station types
CraftStation Tutorial 1: Resources - Learn about creating station types and resources
CraftStation Tutorial 2: Nodes - Learn about CraftStation setup and scripting
CraftStation Tutorial 3: UI - Complete CraftStation UI tutorial