CraftStation Tutorial 2: Nodes
This tutorial continues from CraftStation Tutorial 1: Resources and will guide you through setting up craft station nodes, creating test scenes, and implementing the crafting logic with scripts.
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial, make sure you have:
Completed CraftStation Tutorial 1: Resources
A CraftStationType resource created (Furnace)
Items and recipes set up from the previous tutorial
Setting Up Test Scenes
Step 6: Create a Furnace Scene
Create New Scene
Create a new scene with Node as root (name: “FurnaceTest”).
Add Scene Nodes
CraftStation (name: “FurnaceStation”)
Inventory (name: “InputInventory”)
Inventory (name: “OutputInventory”)
Configure Inventories
Set both inventories:
Database: Your InventoryDatabase
Configure Furnace Station
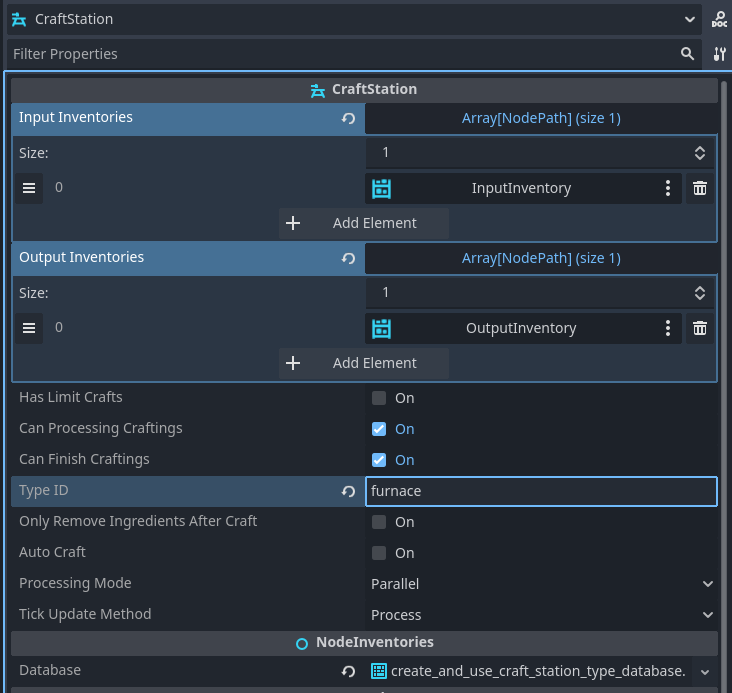
Set the CraftStation properties:
Database: Your InventoryDatabase
Type: Select the “Furnace” CraftStationType
Input Inventories: Add InputInventory path
Output Inventories: Add OutputInventory path
Can Processing Craftings: Enabled
Can Finish Craftings: Enabled
Step 7: Create a General Workbench Scene
Create Another Scene
Create a new scene (name: “WorkbenchTest”).
Add Same Nodes
Add the same node structure as the furnace scene.
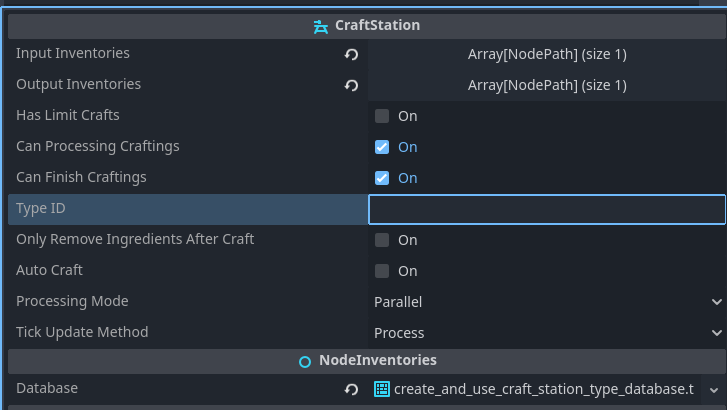
Configure Workbench Station
Set the CraftStation properties the same as furnace, but: - Type: Leave this EMPTY (no station type)
Adding Control Scripts
Step 8: Script the Furnace Scene
Attach this script to the FurnaceTest root node:
extends Node
@onready var craft_station = $FurnaceStation
@onready var input_inventory = $InputInventory
@onready var output_inventory = $OutputInventory
func _ready():
# Add iron ore
input_inventory.add("iron_ore", 10)
# Add coal (fuel)
input_inventory.add("coal", 5)
# Connect signals
craft_station.on_crafted.connect(_on_craft_completed)
# Print station info
print("=== FURNACE STATION ===")
print("Station Type: ", craft_station.type.name if craft_station.type else "None")
print("Available recipes: ", craft_station.valid_recipes.size())
# List available recipes
for i in craft_station.valid_recipes.size():
var recipe_index = craft_station.valid_recipes[i]
var recipe = craft_station.database.recipes[recipe_index]
var product_name = recipe.products[0].item_id if recipe.products.size() > 0 else "Unknown"
print("Recipe ", i, ": ", product_name)
# Check if we can craft it
var can_craft = craft_station.can_craft(recipe)
print(" Can craft: ", can_craft)
func _input(event):
if event.is_action_pressed("ui_accept"):
if craft_station.valid_recipes.size() > 0:
print("Starting furnace smelting...")
craft_station.craft(0)
else:
print("No recipes available!")
func _on_craft_completed(recipe_index: int):
print("Smelting completed!")
# Show output
for i in output_inventory.stacks.size():
var stack = output_inventory.stacks[i]
if stack:
print("Produced: ", stack.amount, "x ", stack.item_id)
Step 9: Script the Workbench Scene
Attach this script to the WorkbenchTest root node:
extends Node
@onready var craft_station = $WorkbenchStation
@onready var input_inventory = $InputInventory
@onready var output_inventory = $OutputInventory
func _ready():
# Add test items
input_inventory.add("wood", 30)
# Connect signals
craft_station.on_crafted.connect(_on_craft_completed)
# Print station info
print("=== WORKBENCH STATION ===")
print("Station Type: ", craft_station.type.name if craft_station.type else "None")
print("Available recipes: ", craft_station.valid_recipes.size())
# List available recipes
for i in craft_station.valid_recipes.size():
var recipe_index = craft_station.valid_recipes[i]
var recipe = craft_station.database.recipes[recipe_index]
var product_name = recipe.products[0].item_id if recipe.products.size() > 0 else "Unknown"
print("Recipe ", i, ": ", product_name)
var can_craft = craft_station.can_craft(recipe)
print(" Can craft: ", can_craft)
func _input(event):
if event.is_action_pressed("ui_accept"):
if craft_station.valid_recipes.size() > 0:
print("Starting crafting...")
craft_station.craft(1)
else:
print("No recipes available!")
func _on_craft_completed(recipe_index: int):
print("Crafting completed!")
# Show output
for i in output_inventory.stacks.size():
var stack = output_inventory.stacks[i]
if stack:
print("Produced: ", stack.amount, "x ", stack.item_id)
Testing Station Types
Step 10: Test the Filtering
Run the Furnace Scene
When you run the furnace scene, you should see: - Station Type: “Furnace” - Available recipes: 1 (only the iron smelting recipe) - The recipe should show “Iron Ingot” - Press Space to start smelting
Run the Workbench Scene
When you run the workbench scene, you should see: - Station Type: “None” - Available recipes: 1 (only the stick crafting recipe) - The recipe should show “Stick” - Press Space to start crafting
Verify Recipe Filtering
This demonstrates that: - Furnace stations only see furnace recipes - General stations only see general recipes - Station types successfully filter available recipes
Advanced Usage
Step 11: Dynamic Station Type Assignment
You can also assign station types in code:
func _ready():
# Assign to station
craft_station.type = "furnace"
Troubleshooting
No Recipes Available
If a station shows no available recipes:
Check that recipe station types match the craft station type
Verify both are using the same CraftStationType resource
Ensure recipes have the correct station type assigned
Wrong Recipes Showing
If the wrong recipes appear:
Double-check recipe station type assignments
Verify craft station type is set correctly
Remember: empty station type only matches other empty station types
Next Steps
Now that you understand how to set up craft station nodes and implement the basic crafting logic, you can continue to the next tutorial to learn how to create a complete UI for your crafting system.
See also
CraftStation Tutorial 1: Resources - Review the resource creation steps
CraftStation Tutorial 3: UI - Build a complete crafting UI